广度优先搜索¶
案例1:队列实现迷宫问题¶
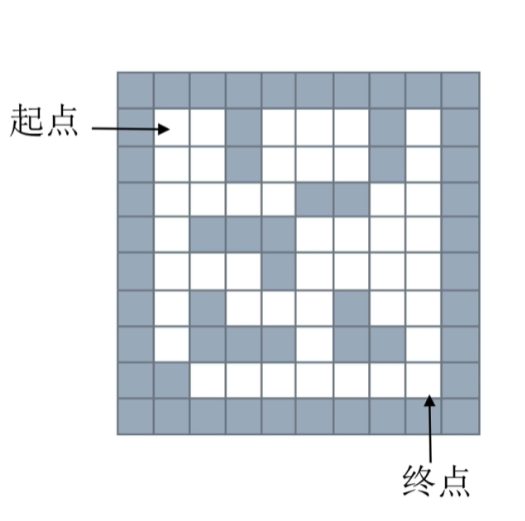
思路 :从起点开始,分成多步(上、下、左、右),并用队列记录这些步。当从某个点走到下一个点时,对该点 出队 ,并将下一步的可能点进队(可能是多个)。最终先到达终点的就是最短路径。每次出队进队时,都需要记录该点是由那个点走来的,这样便可以回溯,从而找到所求路径。
代码实现¶
from collections import deque
def solve(maze , start , end):
queue = deque(maxlen=100)
queue.append(start)
possibleStep = [
lambda i : [i[0] - 1 , i[1] ] ,
lambda i : [i[0] , i[1] + 1] ,
lambda i : [i[0] + 1 , i[1] ] ,
lambda i : [i[0] , i[1] - 1] ,
]
traceBack = {}
traceBack[str(start)] = None
# 标记起点
maze[start[0]][start[1]] = 1
# 队列找终点
while True:
if end in queue:
break
else:
# 原位置出队列
originCoord = queue.popleft()
# 找下一个可能的位置
for i in possibleStep:
nextCoord = i(originCoord)
if maze[nextCoord[0]][nextCoord[1]] == 0: # 可走
# 记录进回溯字典
# 下一步为键,原步为值
traceBack[str(nextCoord)] = str(originCoord)
# 下一步入队列
queue.append(nextCoord)
# 标记为走过
maze[nextCoord[0]][nextCoord[1]] = 1
# 回溯路径
nowCoord = str(end)
res = []
while nowCoord != None:
res.append(nowCoord)
nowCoord = traceBack[nowCoord]
return res